Tabla de Contenidos
Extracción de metadatos en imágenes
Módulo perteneciente al curso Python avanzado para proyectos de seguridad
Exiftool es una aplicación de código abierto que permite leer, escribir y manipular metadatos de imágenes, audio y video.
Se trata de una aplicación que nos permite visualizar los metadatos de una gran cantidad de formatos de imágenes, como AWR, ASF, SVG, TIFF, BMP, CRW, PSD, GIF, XMP, JP2, JPEG, DNG y unos cuantos más. Y en cuanto a los formatos de metadatos soportados podemos mencionar el EXIF, GPS, IPTC, XMP, Kodak, Rico, Adobe, Vorbis, JPEG 2000, Ducky, QuickTime, Matroska y DjVu entre otros.
La aplicación está disponible para Windows, Mac OS X y LInux.
En el caso de una distribución basada en Debian, podríamos instalarla con el comando:
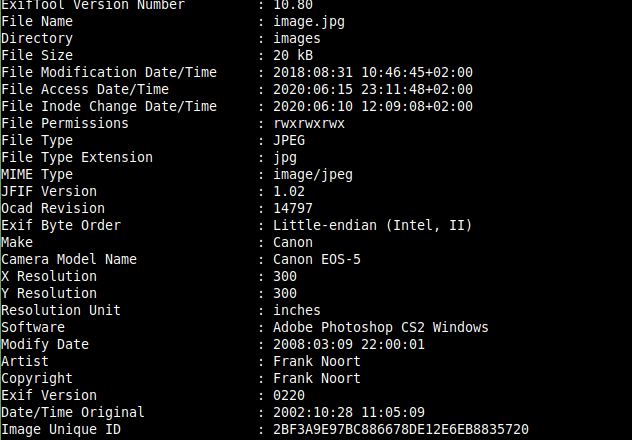
$ sudo apt-get install libimage-exiftool-perl</strong>
Una vez instalada, para su ejecución bastaría con pasar por parámetro la ruta de la imagen:
$ exiftool images/image.jpg</strong>
Extracción de metadatos con el módulo PIL.ExifTags
Uno de los principales módulos que encontramos dentro de Python para el procesamiento y manipulación de imágenes es PIL.
PIL permite extraer los metadatos de imágenes en formato EXIF. Exif (Exchange Image File Format) es una especificación que indica las reglas que deben seguirse cuando vamos a guardar imágenes. Esta especificación es aplicada hoy en día en la mayoría de dispositivos móviles y cámaras digitales.
El módulo PIL.ExifTags permite extraer la información de estas etiquetas. ExifTags contiene una estructura de diccionario con constantes y nombres para muchas etiquetas EXIF conocidas.
Este módulo proporciona 2 clases con las que trabajar:
PIL.ExifTags.TAGS. Permite extraer la etiquetas más comunes almacenadas en la imagen.PIL.ExifTags.GPSTAGS. Permite extraer las etiquetas relacionadas con información de geolocalización.
Por ejemplo, podemos ver todas las etiquetas de las cuales podemos extraer información con el método TAGS.values():
>>> from PIL.ExifTags import TAGS >>> print(TAGS.values()) dict_values(['ProcessingSoftware', 'NewSubfileType', 'SubfileType', 'ImageWidth', 'ImageLength', 'BitsPerSample', 'Compression', 'PhotometricInterpretation', 'Thresholding', 'CellWidth', 'CellLength', 'FillOrder', 'DocumentName', 'ImageDescription', 'Make', 'Model', 'StripOffsets', 'Orientation', 'SamplesPerPixel', 'RowsPerStrip', 'StripByteCounts', 'MinSampleValue', 'MaxSampleValue', 'XResolution', 'YResolution', 'PlanarConfiguration', 'PageName', 'FreeOffsets', 'FreeByteCounts', 'GrayResponseUnit', 'GrayResponseCurve', 'T4Options', 'T6Options', 'ResolutionUnit', 'PageNumber', 'TransferFunction', 'Software', 'DateTime', 'Artist', 'HostComputer', 'Predictor', 'WhitePoint', 'PrimaryChromaticities', 'ColorMap', 'HalftoneHints', 'TileWidth', 'TileLength', 'TileOffsets', 'TileByteCounts', 'SubIFDs', 'InkSet', 'InkNames', 'NumberOfInks', 'DotRange', 'TargetPrinter', 'ExtraSamples', 'SampleFormat', 'SMinSampleValue', 'SMaxSampleValue', 'TransferRange', 'ClipPath', 'XClipPathUnits', 'YClipPathUnits', 'Indexed', 'JPEGTables', 'OPIProxy', 'JPEGProc', 'JpegIFOffset', 'JpegIFByteCount', 'JpegRestartInterval', 'JpegLosslessPredictors', 'JpegPointTransforms', 'JpegQTables', 'JpegDCTables', 'JpegACTables', 'YCbCrCoefficients', 'YCbCrSubSampling', 'YCbCrPositioning', 'ReferenceBlackWhite', 'XMLPacket', 'RelatedImageFileFormat', 'RelatedImageWidth', 'RelatedImageLength', 'Rating', 'RatingPercent', 'ImageID', 'CFARepeatPatternDim', 'CFAPattern', 'BatteryLevel', 'Copyright', 'ExposureTime', 'FNumber', 'IPTCNAA', 'ImageResources', 'ExifOffset', 'InterColorProfile', 'ExposureProgram', 'SpectralSensitivity', 'GPSInfo', 'ISOSpeedRatings', 'OECF', 'Interlace', 'TimeZoneOffset', 'SelfTimerMode', 'ExifVersion', 'DateTimeOriginal', 'DateTimeDigitized', 'ComponentsConfiguration', 'CompressedBitsPerPixel', 'ShutterSpeedValue', 'ApertureValue', 'BrightnessValue', 'ExposureBiasValue', 'MaxApertureValue', 'SubjectDistance', 'MeteringMode', 'LightSource', 'Flash', 'FocalLength', 'FlashEnergy', 'SpatialFrequencyResponse', 'Noise', 'ImageNumber', 'SecurityClassification', 'ImageHistory', 'SubjectLocation', 'ExposureIndex', 'TIFF/EPStandardID', 'MakerNote', 'UserComment', 'SubsecTime', 'SubsecTimeOriginal', 'SubsecTimeDigitized', 'XPTitle', 'XPComment', 'XPAuthor', 'XPKeywords', 'XPSubject', 'FlashPixVersion', 'ColorSpace', 'ExifImageWidth', 'ExifImageHeight', 'RelatedSoundFile', 'ExifInteroperabilityOffset', 'FlashEnergy', 'SpatialFrequencyResponse', 'FocalPlaneXResolution', 'FocalPlaneYResolution', 'FocalPlaneResolutionUnit', 'SubjectLocation', 'ExposureIndex', 'SensingMethod', 'FileSource', 'SceneType', 'CFAPattern', 'CustomRendered', 'ExposureMode', 'WhiteBalance', 'DigitalZoomRatio', 'FocalLengthIn35mmFilm', 'SceneCaptureType', 'GainControl', 'Contrast', 'Saturation', 'Sharpness', 'DeviceSettingDescription', 'SubjectDistanceRange', 'ImageUniqueID', 'CameraOwnerName', 'BodySerialNumber', 'LensSpecification', 'LensMake', 'LensModel', 'LensSerialNumber', 'Gamma', 'PrintImageMatching', 'DNGVersion', 'DNGBackwardVersion', 'UniqueCameraModel', 'LocalizedCameraModel', 'CFAPlaneColor', 'CFALayout', 'LinearizationTable', 'BlackLevelRepeatDim', 'BlackLevel', 'BlackLevelDeltaH', 'BlackLevelDeltaV', 'WhiteLevel', 'DefaultScale', 'DefaultCropOrigin', 'DefaultCropSize', 'ColorMatrix1', 'ColorMatrix2', 'CameraCalibration1', 'CameraCalibration2', 'ReductionMatrix1', 'ReductionMatrix2', 'AnalogBalance', 'AsShotNeutral', 'AsShotWhiteXY', 'BaselineExposure', 'BaselineNoise', 'BaselineSharpness', 'BayerGreenSplit', 'LinearResponseLimit', 'CameraSerialNumber', 'LensInfo', 'ChromaBlurRadius', 'AntiAliasStrength', 'ShadowScale', 'DNGPrivateData', 'MakerNoteSafety', 'CalibrationIlluminant1', 'CalibrationIlluminant2', 'BestQualityScale', 'RawDataUniqueID', 'OriginalRawFileName', 'OriginalRawFileData', 'ActiveArea', 'MaskedAreas', 'AsShotICCProfile', 'AsShotPreProfileMatrix', 'CurrentICCProfile', 'CurrentPreProfileMatrix', 'ColorimetricReference', 'CameraCalibrationSignature', 'ProfileCalibrationSignature', 'AsShotProfileName', 'NoiseReductionApplied', 'ProfileName', 'ProfileHueSatMapDims', 'ProfileHueSatMapData1', 'ProfileHueSatMapData2', 'ProfileToneCurve', 'ProfileEmbedPolicy', 'ProfileCopyright', 'ForwardMatrix1', 'ForwardMatrix2', 'PreviewApplicationName', 'PreviewApplicationVersion', 'PreviewSettingsName', 'PreviewSettingsDigest', 'PreviewColorSpace', 'PreviewDateTime', 'RawImageDigest', 'OriginalRawFileDigest', 'SubTileBlockSize', 'RowInterleaveFactor', 'ProfileLookTableDims', 'ProfileLookTableData', 'OpcodeList1', 'OpcodeList2', 'OpcodeList3', 'NoiseProfile'])
De la misma forma podemos las etiquetas relacionadas con geolocalización con el método GPSTAGS.values():
>>> from PIL.ExifTags import GPSTAGS >>> print(GPSTAGS.values()) dict_values(['GPSVersionID', 'GPSLatitudeRef', 'GPSLatitude', 'GPSLongitudeRef', 'GPSLongitude', 'GPSAltitudeRef', 'GPSAltitude', 'GPSTimeStamp', 'GPSSatellites', 'GPSStatus', 'GPSMeasureMode', 'GPSDOP', 'GPSSpeedRef', 'GPSSpeed', 'GPSTrackRef', 'GPSTrack', 'GPSImgDirectionRef', 'GPSImgDirection', 'GPSMapDatum', 'GPSDestLatitudeRef', 'GPSDestLatitude', 'GPSDestLongitudeRef', 'GPSDestLongitude', 'GPSDestBearingRef', 'GPSDestBearing', 'GPSDestDistanceRef', 'GPSDestDistance', 'GPSProcessingMethod', 'GPSAreaInformation', 'GPSDateStamp', 'GPSDifferential', 'GPSHPositioningError'])
Obtener los metadatos EXIF de una imagen
Primero importamos los módulos PIL y PIL.ExifTags. PIL es un módulo de procesamiento de imágenes en Python que soporta diferentes formatos de archivo y tiene una poderosa capacidad de procesamiento de imágenes.
Para obtener la información de EXIF tags de una imagen se puede utilizar el método _getexif() del objeto imagen.
Este método nos devuelve una estructura diccionario que podemos recorrer con el método items().
Puede encontrar el siguiente código en el archivo get_exif_tags.py:
from PIL import Image from PIL.ExifTags import TAGS print(Image.open('images/image.jpg')._getexif()) for (key,value) in Image.open('images/image.jpg')._getexif().items(): print('%s = %s' % (TAGS.get(key), value))
Por ejemplo, podemos tener una función donde a partir de la ruta de la imagen nos devuelva información de EXIF tags.
Puede encontrar el siguiente código en el archivo extractDataFromImages.py:
def get_exif_metadata(image_path): exifData = {} image = Image.open(image_path) if hasattr(image, '_getexif'): exifinfo = image._getexif() if exifinfo is not None: for tag, value in exifinfo.items(): decoded = TAGS.get(tag, tag) exifData[decoded] = value decode_gps_info2(exifData) return exifData
Obteniendo geolocalización
En el ejemplo anterior vemos que hemos obtenido también información en el objeto GPSInfo acerca de la localización de la imagen. Esta información se puede mejorar descodificando la información que hemos obtenido en un formato de valores latitud/longitud, para ellos podemos hacer una función que dado un atributo exif del tipo GPSInfo, nos descodifique esa información.
def decode_gps_info2(exif): gpsinfo = {} if 'GPSInfo' in exif: for key in exif['GPSInfo'].keys(): decode = GPSTAGS.get(key,key) gpsinfo[decode] = exif['GPSInfo'][key] print(gpsinfo) exif['GPSInfo'] = gpsinfo
Otra forma de parsear la información correspondiente a la geolocalización es a través de este método, que sería equivalente al estudiado anteriormente.
def decode_gps_info(exif): gpsinfo = {} if 'GPSInfo' in exif: ''' Raw Geo-references for key in exif['GPSInfo'].keys(): decode = GPSTAGS.get(key,key) gpsinfo[decode] = exif['GPSInfo'][key] exif['GPSInfo'] = gpsinfo ''' #Parse geo references. Nsec = exif['GPSInfo'][2][2][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][2][2][1]) Nmin = exif['GPSInfo'][2][1][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][2][1][1]) Ndeg = exif['GPSInfo'][2][0][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][2][0][1]) Wsec = exif['GPSInfo'][4][2][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][4][2][1]) Wmin = exif['GPSInfo'][4][1][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][4][1][1]) Wdeg = exif['GPSInfo'][4][0][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][4][0][1]) if exif['GPSInfo'][1] == 'N': Nmult = 1 else: Nmult = -1 if exif['GPSInfo'][1] == 'E': Wmult = 1 else: Wmult = -1 Lat = Nmult * (Ndeg + (Nmin + Nsec/60.0)/60.0) Lng = Wmult * (Wdeg + (Wmin + Wsec/60.0)/60.0) exif['GPSInfo'] = {"Lat" : Lat, "Lng" : Lng}
En el script anterior, analizamos los datos Exif en una matriz, indexados por el tipo de metadatos. Con la matriz completa, podemos buscar la matriz para ver si contiene una etiqueta Exif para GPSInfo. Si contiene una etiqueta GPSInfo, sabremos que el objeto contiene metadatos GPS y podremos imprimir un mensaje en la pantalla.
En la siguiente salida podemos ver que también hemos obtenido información en el objeto GPSInfo sobre la ubicación de la imagen:
[+] Metadata for file: images/image.jpg
{'GPSVersionID': b'\x00\x00\x02\x02', 'GPSLatitudeRef': 'N', 'GPSLatitude': ((32, 1), (4, 1), (4349, 100)), 'GPSLongitudeRef': 'E', 'GPSLongitude': ((131, 1), (28, 1), (328, 100)), 'GPSAltitudeRef': b'\x00', 'GPSAltitude': (0, 1)}
Metadata: GPSInfo - Value: {'GPSVersionID': b'\x00\x00\x02\x02', 'GPSLatitudeRef': 'N', 'GPSLatitude': ((32, 1), (4, 1), (4349, 100)), 'GPSLongitudeRef': 'E', 'GPSLongitude': ((131, 1), (28, 1), (328, 100)), 'GPSAltitudeRef': b'\x00', 'GPSAltitude': (0, 1)}
Metadata: ResolutionUnit - Value: 2
Metadata: ExifOffset - Value: 146
Metadata: Make - Value: Canon
Metadata: Model - Value: Canon EOS-5
Metadata: Software - Value: Adobe Photoshop CS2 Windows
Metadata: DateTime - Value: 2008:03:09 22:00:01
Metadata: Artist - Value: Frank Noort
Metadata: Copyright - Value: Frank Noort
Metadata: XResolution - Value: (300, 1)
Metadata: YResolution - Value: (300, 1)
Metadata: ExifVersion - Value: b'0220'
Metadata: ImageUniqueID - Value: 2BF3A9E97BC886678DE12E6EB8835720
Metadata: DateTimeOriginal - Value: 2002:10:28 11:05:09
Actividad práctica: Completar el código que permite obtener los metadatos de todas las imágenes que se encuentran dentro del directorio imágenes
Completar el código que permite obtener los metadatos de la imagen que se encuentran dentro del directorio images.
#!/usr/bin/env python from PIL import xxx from PIL.ExifTags import xxx def get_exif_tags(path_image): resultado = {} image = Image.xxx(xxx) info = image.xxx() for tag, value in info.xxx(): decoded = xxx.get(xxx, xxx) resultado[xxx] = xxx return xxx tags = get_exif_tags('images/image.jpg') for (key,value) in xxx.xxx(): print('%s = %s' % (xxx,xxx))
La salida del script con los metadatos de la image podría ser:
GPSInfo = {0: b'\x00\x00\x02\x02', 1: 'N', 2: ((32, 1), (4, 1), (4349, 100)), 3: 'E', 4: ((131, 1), (28, 1), (328, 100)), 5: b'\x00', 6: (0, 1)}
ResolutionUnit = 2
ExifOffset = 146
Make = Canon
Model = Canon EOS-5
Software = Adobe Photoshop CS2 Windows
DateTime = 2008:03:09 22:00:01
Artist = Frank Noort
Copyright = Frank Noort
XResolution = (300, 1)
YResolution = (300, 1)
ExifVersion = b'0220'
ImageUniqueID = 2BF3A9E97BC886678DE12E6EB8835720
DateTimeOriginal = 2002:10:28 11:05:09
Solución
#!/usr/bin/env python from PIL import Image from PIL.ExifTags import TAGS def get_exif_tags(path_image): resultado = {} image = Image.open(path_image) info = image._getexif() for tag, value in info.items(): decoded = TAGS.get(tag, tag) resultado[decoded] = value return resultado tags = get_exif_tags('images/image.jpg') for (key,value) in tags.items(): print('%s = %s' % (key,value))
Extraer metadatos de imágenes web
En esta sección, vamos a crear un script para conectarse a un sitio web, descargar todas las imágenes en el sitio y luego verificar si hay metadatos Exif.
Para esta tarea, estamos utilizando el módulo urllib de python3 que proporciona los paquetes de parse y request:
Puede encontrar el siguiente código en el archivo exif_images_web_page.py. Este script contiene los métodos para buscar imágenes en un sitio web con el parser BeautifulSoup y descargar las imágenes en una carpeta.
Primero añadimos los imports necesarios:
from urllib.request import urlopen from urllib.parse import urlparse,urlsplit import requests import optparse from os.path import basename from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from PIL import Image from PIL.ExifTags import TAGS import os
El método findImages(url) permite obtenerlas imágenes de un sitio, para ello recibe por parámetro la url y utilizando los módulos requests y BeautifulSoup, realiza la petición y parsea el contenido html para obtener las imágenes.
def findImages(url): print('[+] Finding images on ' + url) urlContent = requests.get(url).text print(urlContent) soup = BeautifulSoup(urlContent,'lxml') imgTags = soup.findAll('img') return imgTags
El método downloadImage(imgTag,url) permite descargar la imagen en el directorio de images.
def downloadImage(imgTag,url): try: print('[+] Dowloading in images directory...'+imgTag['src']) imgSrc = url+imgTag['src'] imgContent = urlopen(imgSrc).read() imgFileName = basename(urlsplit(imgSrc)[2]) imgFile = open('images/'+imgFileName, 'wb') imgFile.write(imgContent) imgFile.close() return imgFileName except Exception as e: print(e) return ''
Script completo añadiendo también la geolocalización:
#!/usr/bin/env python from urllib.request import urlopen from urllib.parse import urlparse,urlsplit import requests import optparse from os.path import basename from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from PIL import Image from PIL.ExifTags import TAGS import os def findImages(url): print('[+] Finding images on ' + url) urlContent = requests.get(url).text print(urlContent) soup = BeautifulSoup(urlContent,'lxml') imgTags = soup.findAll('img') return imgTags def downloadImage(imgTag,url): try: print('[+] Dowloading in images directory...'+imgTag['src']) imgSrc = url+imgTag['src'] imgContent = urlopen(imgSrc).read() imgFileName = basename(urlsplit(imgSrc)[2]) imgFile = open('images/'+imgFileName, 'wb') imgFile.write(imgContent) imgFile.close() return imgFileName except Exception as e: print(e) return '' def decode_gps_info(exif): gpsinfo = {} if 'GPSInfo' in exif: ''' Raw Geo-references for key in exif['GPSInfo'].keys(): decode = GPSTAGS.get(key,key) gpsinfo[decode] = exif['GPSInfo'][key] exif['GPSInfo'] = gpsinfo ''' #Parse geo references. Nsec = exif['GPSInfo'][2][2][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][2][2][1]) Nmin = exif['GPSInfo'][2][1][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][2][1][1]) Ndeg = exif['GPSInfo'][2][0][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][2][0][1]) Wsec = exif['GPSInfo'][4][2][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][4][2][1]) Wmin = exif['GPSInfo'][4][1][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][4][1][1]) Wdeg = exif['GPSInfo'][4][0][0] / float(exif['GPSInfo'][4][0][1]) if exif['GPSInfo'][1] == 'N': Nmult = 1 else: Nmult = -1 if exif['GPSInfo'][1] == 'E': Wmult = 1 else: Wmult = -1 Lat = Nmult * (Ndeg + (Nmin + Nsec/60.0)/60.0) Lng = Wmult * (Wdeg + (Wmin + Wsec/60.0)/60.0) exif['GPSInfo'] = {"Lat" : Lat, "Lng" : Lng} def get_exif_metadata(image_path): print(image_path) exifData = {} image = Image.open(image_path) if hasattr(image, '_getexif'): exifinfo = image._getexif() if exifinfo is not None: for tag, value in exifinfo.items(): decoded = TAGS.get(tag, tag) exifData[decoded] = value decode_gps_info(exifData) return exifData def printMetadata(): print("Extracting metadata from images in images directory.........") for dirpath, dirnames, files in os.walk("images"): for name in files: print("[+] Metadata for file: %s " %(dirpath+os.path.sep+name)) try: exifData = {} exif = get_exif_metadata(dirpath+os.path.sep+name) for metadata in exif: print("Metadata: %s - Value: %s " %(metadata, exif[metadata])) print("\n") except: import sys, traceback traceback.print_exc(file=sys.stdout) def main(): parser = optparse.OptionParser('--url <target url>') parser.add_option('--url', dest='url', type='string', help='specify url address') (options, args) = parser.parse_args() url = options.url if url == None: print(parser.usage) exit(0) else: imgTags = findImages(url) print(imgTags) for imgTag in imgTags: imgFileName = downloadImage(imgTag,url) printMetadata() if __name__ == '__main__': main()
Extrayendo metatados de las imágenes descargadas
Esta es la función que extrae metadatos de las imágenes que se hayan descargado dentro del directorio de imágenes:
def printMetadata(): print("Extracting metadata from images in images directory.........") for dirpath, dirnames, files in os.walk("images"): for name in files: print("[+] Metadata for file: %s " %(dirpath+os.path.sep+name)) try: exifData = {} exif = get_exif_metadata(dirpath+os.path.sep+name) for metadata in exif: print("Metadata: %s - Value: %s " %(metadata, exif[metadata])) print("\n") except: import sys, traceback traceback.print_exc(file=sys.stdout)
Este es nuestro método principal que obtiene una url como argumento de entrada y llama a los métodos findImages(url), downloadImage(imgTags,url) y printMetadata():
def main(): parser = optparse.OptionParser('--url <target url>') parser.add_option('--url', dest='url', type='string', help='specify url address') (options, args) = parser.parse_args() url = options.url if url == None: print(parser.usage) exit(0) else: imgTags = findImages(url) print(imgTags) for imgTag in imgTags: imgFileName = downloadImage(imgTag,url) printMetadata()
FAQ
¿Para qué sirve la herramienta exiftool?
ExifTool es un programa de software gratuito y de código abierto para leer, escribir y manipular metadatos de imagen, audio, video y PDF. Es independiente de la plataforma, disponible como una biblioteca Perl y una aplicación de línea de comandos.